Sodium »
PDB 2ekb-2fm1 »
2f53 »
Sodium in PDB 2f53: Directed Evolution of Human T-Cell Receptor CDR2 Residues By Phage Display Dramatically Enhances Affinity For Cognate Peptide-Mhc Without Apparent Cross-Reactivity
Protein crystallography data
The structure of Directed Evolution of Human T-Cell Receptor CDR2 Residues By Phage Display Dramatically Enhances Affinity For Cognate Peptide-Mhc Without Apparent Cross-Reactivity, PDB code: 2f53
was solved by
P.J.Rizkallah,
B.K.Jakobsen,
S.M.Dunn,
M.Sami,
with X-Ray Crystallography technique. A brief refinement statistics is given in the table below:
| Resolution Low / High (Å) | 37.85 / 2.10 |
| Space group | P 1 21 1 |
| Cell size a, b, c (Å), α, β, γ (°) | 76.234, 53.972, 119.905, 90.00, 96.83, 90.00 |
| R / Rfree (%) | 16.6 / 23.1 |
Sodium Binding Sites:
The binding sites of Sodium atom in the Directed Evolution of Human T-Cell Receptor CDR2 Residues By Phage Display Dramatically Enhances Affinity For Cognate Peptide-Mhc Without Apparent Cross-Reactivity
(pdb code 2f53). This binding sites where shown within
5.0 Angstroms radius around Sodium atom.
In total only one binding site of Sodium was determined in the Directed Evolution of Human T-Cell Receptor CDR2 Residues By Phage Display Dramatically Enhances Affinity For Cognate Peptide-Mhc Without Apparent Cross-Reactivity, PDB code: 2f53:
In total only one binding site of Sodium was determined in the Directed Evolution of Human T-Cell Receptor CDR2 Residues By Phage Display Dramatically Enhances Affinity For Cognate Peptide-Mhc Without Apparent Cross-Reactivity, PDB code: 2f53:
Sodium binding site 1 out of 1 in 2f53
Go back to
Sodium binding site 1 out
of 1 in the Directed Evolution of Human T-Cell Receptor CDR2 Residues By Phage Display Dramatically Enhances Affinity For Cognate Peptide-Mhc Without Apparent Cross-Reactivity
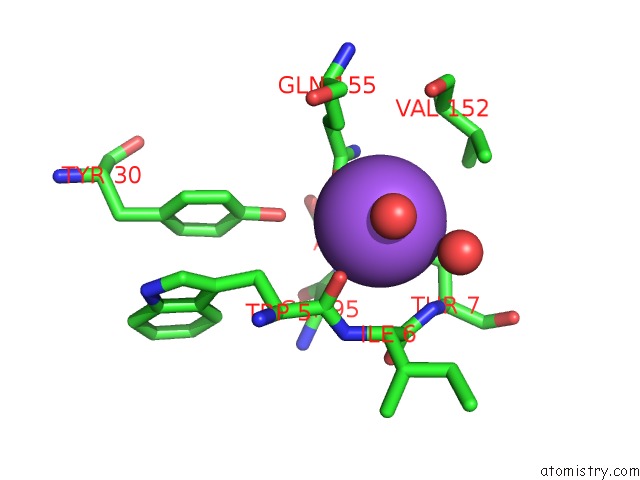
Mono view
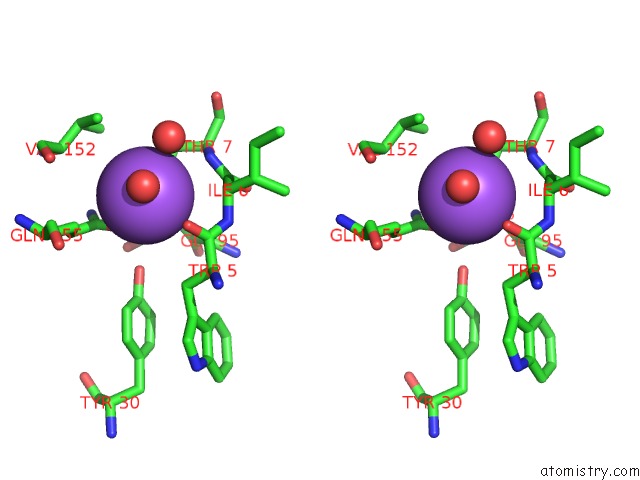
Stereo pair view

Mono view

Stereo pair view
A full contact list of Sodium with other atoms in the Na binding
site number 1 of Directed Evolution of Human T-Cell Receptor CDR2 Residues By Phage Display Dramatically Enhances Affinity For Cognate Peptide-Mhc Without Apparent Cross-Reactivity within 5.0Å range:
|
Reference:
S.M.Dunn,
P.J.Rizkallah,
E.Baston,
T.Mahon,
B.Cameron,
R.Moysey,
F.Gao,
M.Sami,
J.Boulter,
Y.Li,
B.K.Jakobsen.
Directed Evolution of Human T Cell Receptor CDR2 Residues By Phage Display Dramatically Enhances Affinity For Cognate Peptide-Mhc Without Increasing Apparent Cross-Reactivity. Protein Sci. V. 15 710 2006.
ISSN: ISSN 0961-8368
PubMed: 16600963
DOI: 10.1110/PS.051936406
Page generated: Sun Aug 17 10:29:24 2025
ISSN: ISSN 0961-8368
PubMed: 16600963
DOI: 10.1110/PS.051936406
Last articles
Mn in 9LJUMn in 9LJW
Mn in 9LJS
Mn in 9LJR
Mn in 9LJT
Mn in 9LJV
Mg in 9UA2
Mg in 9R96
Mg in 9VM1
Mg in 9P01